|
yumapro
25.10-3
YumaPro SDK
|
 |
yumapro
25.10-3
YumaPro SDK
|
YControl message parsing supports XML encoded communications between the main server and a subsystem. More...

Functions | |
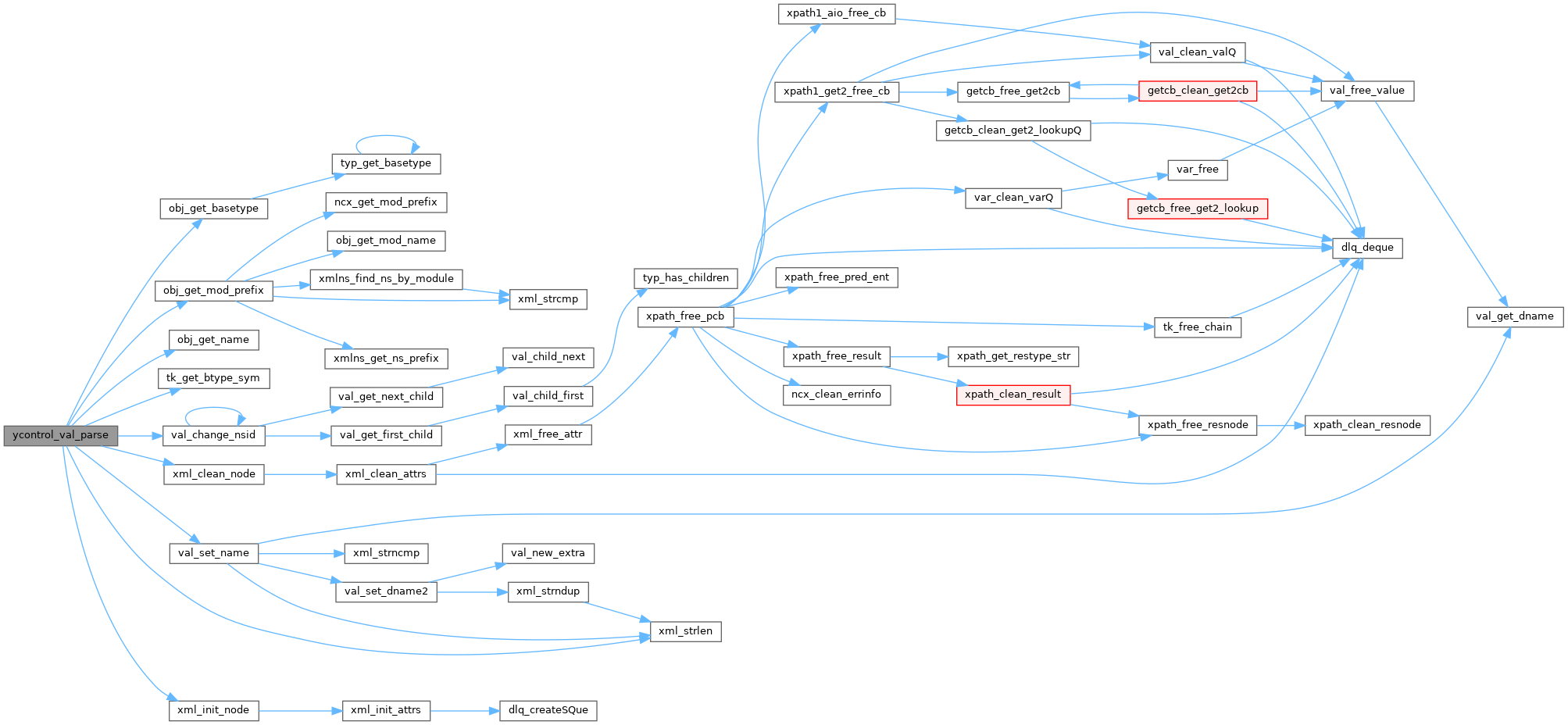
| status_t | ycontrol_val_parse (ses_cb_t *scb, obj_template_t *obj, xml_node_t *startnode, val_value_t *retval) |
| parse a value for a YANG type from a NETCONF PDU XML stream More... | |
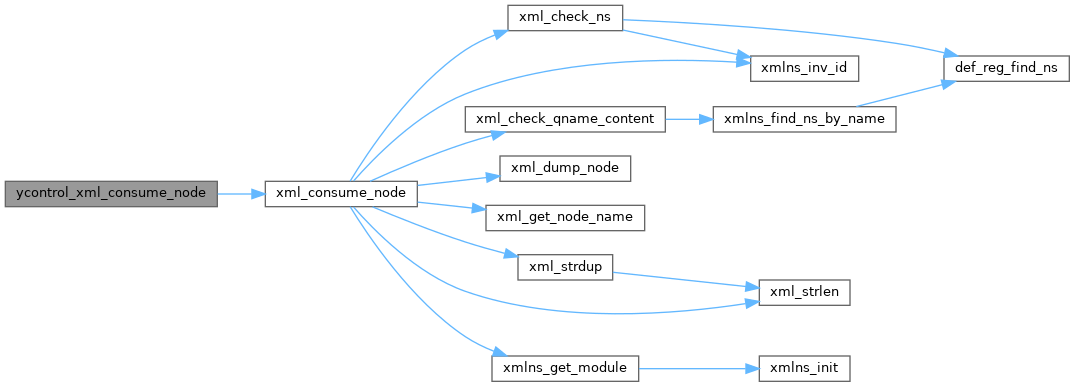
| status_t | ycontrol_xml_consume_node (xmlTextReaderPtr reader, xml_node_t *node) |
| Consume an XML node from the XmlTextReader. More... | |
| status_t | ycontrol_xml_consume_node_nons (xmlTextReaderPtr reader, xml_node_t *node) |
| consume node but do not generate namespace errors if seen. More... | |
| status_t | ycontrol_xml_consume_node_noadv (xmlTextReaderPtr reader, xml_node_t *node) |
| re-get the current node More... | |
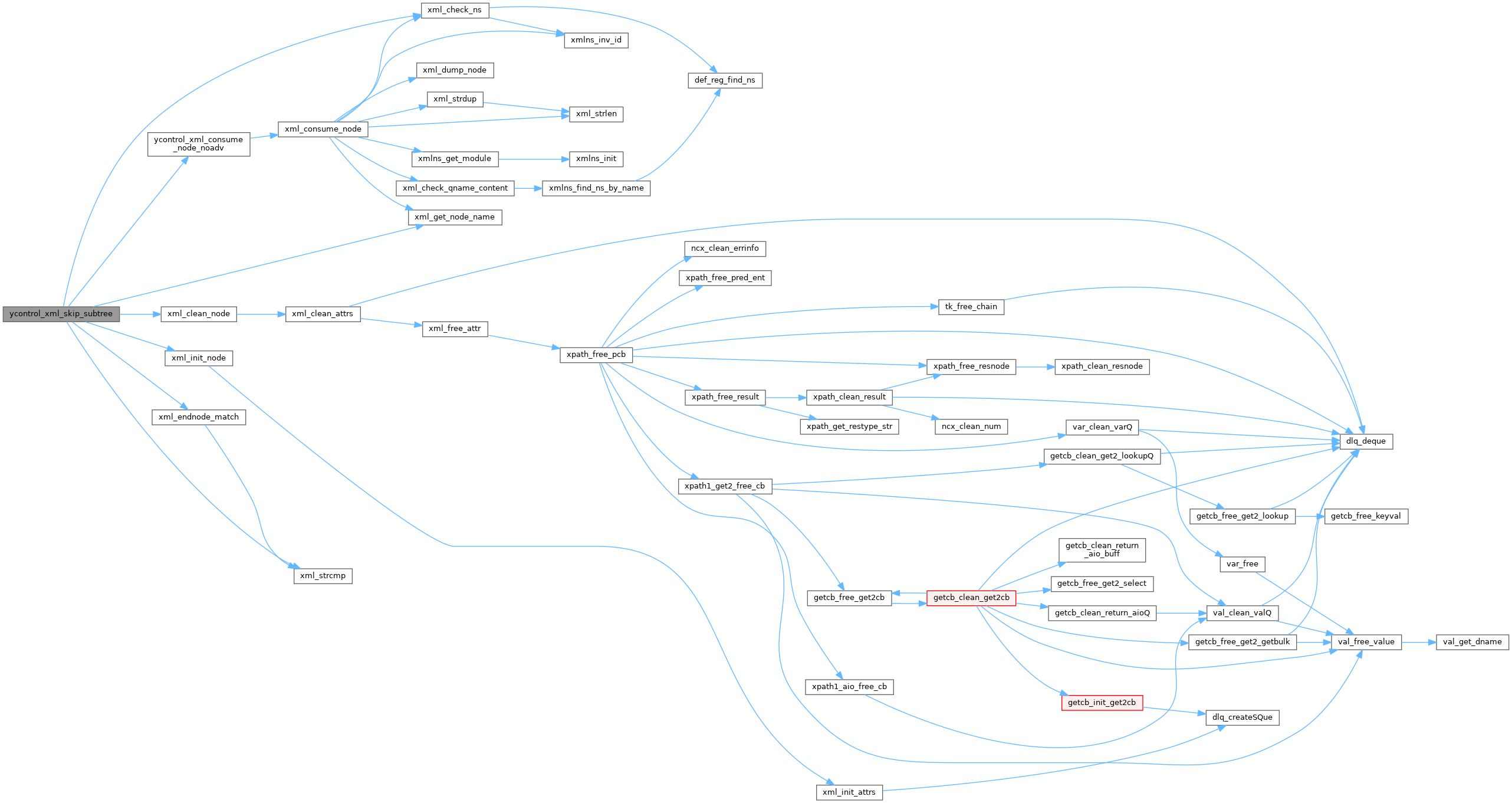
| status_t | ycontrol_xml_skip_subtree (xmlTextReaderPtr reader, const xml_node_t *startnode) |
| Skip the current subtree (due to parse or schema error) More... | |
YControl message parsing supports XML encoded communications between the main server and a subsystem.
In the future other encodings will be supported. The YANG module yumaworks-ycontrol is used to parse the top-level ycontrol element.
| status_t ycontrol_val_parse | ( | ses_cb_t * | scb, |
| obj_template_t * | obj, | ||
| xml_node_t * | startnode, | ||
| val_value_t * | retval | ||
| ) |
parse a value for a YANG type from a NETCONF PDU XML stream
Parse NETCONF PDU sub-contents into value fields This module does not enforce complex type completeness. Different subsets of configuration data are permitted in several standard (and any proprietary) RPC methods
A seperate parsing phase is used to validate the input contained in the returned val_value_t struct.
This parsing phase checks that simple types are complete and child members of complex types are valid (but maybe missing or incomplete child nodes.
| scb | session control block | |
| obj | obj_template_t for the object type to parse | |
| startnode | top node of the parameter to be parsed | |
| [out] | retval | val_value_t that should get the results of the parsing
|
| status_t ycontrol_xml_consume_node | ( | xmlTextReaderPtr | reader, |
| xml_node_t * | node | ||
| ) |
Consume an XML node from the XmlTextReader.
Parse the next node and return its namespace, type and name The xml_init_node or xml_clean_node API must be called before this function for the node parameter
There are 2 types of XML element start nodes
There is one string content node for simpleType content
There is one end node to end both simple and complex types
If nodetyp==XML_NT_EMPTY, then no further nodes will occur for this element. This node may contain attributes. The naming parameters will all be set.
If nodetyp==XML_NT_START, then the caller should examine the schema for that start node. For complex types, the next node is probably another XML_NT_START. For simple types, the next node will be XML_NT_STRING, followed by an XML_NT_END node. This node may contain attributes. The naming parameters will all be set.
If the nodetype==XML_NT_STRING, then the simval and simlen fields will be set. There are no attributes or naming parameters for this node type.
IF the nodetype==XML_NT_END, then no further nodes for this element will occur. This node should not contain attributes. All of the naming parameters will be set. The xml_endnode_match function should be used to confirm that the XML_NT_START and XML_NT_END nodes are paired correctly.
The node pointer for the reader will be advanced before the node is read.
The reader will be advanced.
| reader | XmlReader already initialized from File, Memory, or whatever | |
| [in,out] | node | pointer to an initialized xml_node_t struct to be filled in
|

| status_t ycontrol_xml_consume_node_noadv | ( | xmlTextReaderPtr | reader, |
| xml_node_t * | node | ||
| ) |
re-get the current node
The reader will not be advanced!
| reader | XmlReader already initialized from File, Memory, or whatever | |
| [in,out] | node | pointer to an initialized xml_node_t struct to be filled in
|
| status_t ycontrol_xml_consume_node_nons | ( | xmlTextReaderPtr | reader, |
| xml_node_t * | node | ||
| ) |
consume node but do not generate namespace errors if seen.
needed to process subtree filters properly, No namespace error variant.
The reader will be advanced.
| reader | XmlReader already initialized from File, Memory, or whatever | |
| [in,out] | node | pointer to an initialized xml_node_t struct to be filled in
|
| status_t ycontrol_xml_skip_subtree | ( | xmlTextReaderPtr | reader, |
| const xml_node_t * | startnode | ||
| ) |
Skip the current subtree (due to parse or schema error)
Already encountered an error, so advance nodes until the matching start-node is reached or a terminating error occurs
The xmlreader state is advanced until the current node is the end node of the specified start node or a fatal error occurs
| reader | XmlReader already initialized from File, Memory, or whatever |
| startnode | xml_node_t of the start node of the sub-tree to skip |